- Home
- Services
- Conceptual Design
- Digital Twin Simulation & Emulation
- Manufacturing Flow Design
- Maveneer WxS™
- MavenSHIELD™
- Operational Assessment
- Operational Augmentation
- Process Standardization & Compliance
- Retrofit Design & Modernization
- Supply Chain & Inventory Management
- Supply Chain Network Analysis & Optimization
- Systems Integration
- Warehouse Optimization & Performance Monitoring
- WMS & WES Selection & Strategy
- Workforce Training & Development
- 3D Integrated Modeling
- Industries
- Solutions
- Autostore
- Automated Print and Apply
- Automation as a Service
- Autonomous Mobile Robots
- Automated Guided Vehicles
- Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
- Control System Integration
- Conveyor Systems
- Packaging Automation
- Palletizing
- Depalletizing
- Sortation Systems
- Microfulfillment
- Omnichannel Fulfillment
- eCommerce Fulfillment
- Order Picking
- Robotic Vision Systems
- Warehouse Execution Systems
- Warehouse Storage Racking Solutions
- Resources
- Company
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems, also known as AS/RS, is a category of warehouse automation that uses mechanical retrieval systems to buffer, store, and pick inventory, increasing throughput and storage density while reducing manual labor costs.
Maveneer partners with trusted AS/RS manufacturers to bring the benefits of automation to your warehouse:



Automated Storage and Retrieval System
What is an Automated Storage and Retrieval System (AS/RS)?
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems, also known as AS/RS, is a broad category of warehouse automations. Most AS/RS are used in GTP (Goods-to-Person) environments, where operators remain in one location, and technology and machines bring them the items that they need.
Storage & Retrieval
As the name suggests, automated storage and retrieval systems have two main purposes: to store and retrieve items and inventory.
- Storage: An Automated Storage and Retrieval System is used to store items and inventory at any stage of the order fulfillment process and in a variety of industries—from consolidating and holding orders to managing parts before assembly. AS/RS are commonly used as buffer storage, to safely hold inventory and items in an organized manner, until they’re needed for the next step in a process.
- Retrieval: An Automated Storage and Retrieval System is also used to retrieve items from their storage area, reducing the manual labor required for picking items. Often, an AS/RS is used to bring a product directly to the operator, saving the operator time and walking distance. Some automated storage and retrieval systems are able to retrieve multiple items and bring them to the operator in one ‘trip’, increasing order accuracy and efficiency in addition to reducing labor costs.
Types of Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems
There are a variety of technologies that fall into the category of AS/RS, but they all share similar properties. Most AS/RS utilize densely-stacked racks to store products, and the retrieval equipment integrates with a warehouse management system (WMS) to find and retrieve the products from the racks. There are a variety of AS/RS Solutions, usually categorized by the type of picking that they use. Some systems only bring specific products to their operator, while other systems bring bins, totes or even shelves. Here are the most common types of Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems:
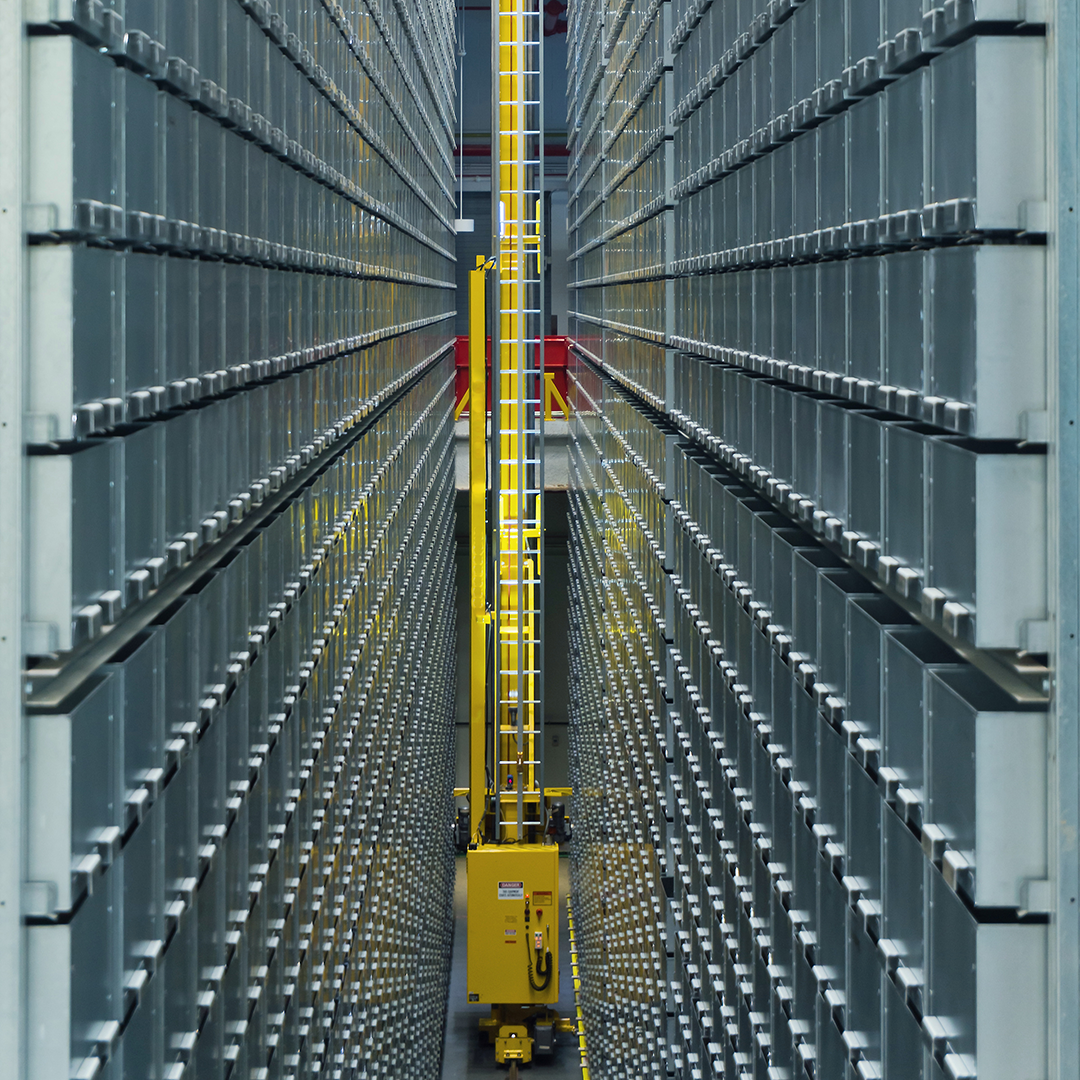

LOAD SYSTEMS
Unit-load and mini-load systems are two of the most common types of automations that are categorized as AS/RS. Both these systems utilize computer-controlled cranes that navigate to a product’s location within the storage area and remove the storage medium where the product is contained. Unit-Load Systems are used to store and retrieve entire pallets, while mini-load systems are used to store and retrieve smaller loads like bins or totes.
Pros: Load systems automate loading and unloading, speeding up the process and reducing manual labor. They improve consistency and efficiency in handling products.
Cons: They require large floor space and significant infrastructure, making them less suitable for smaller warehouses or spaces with fluctuating inventory.
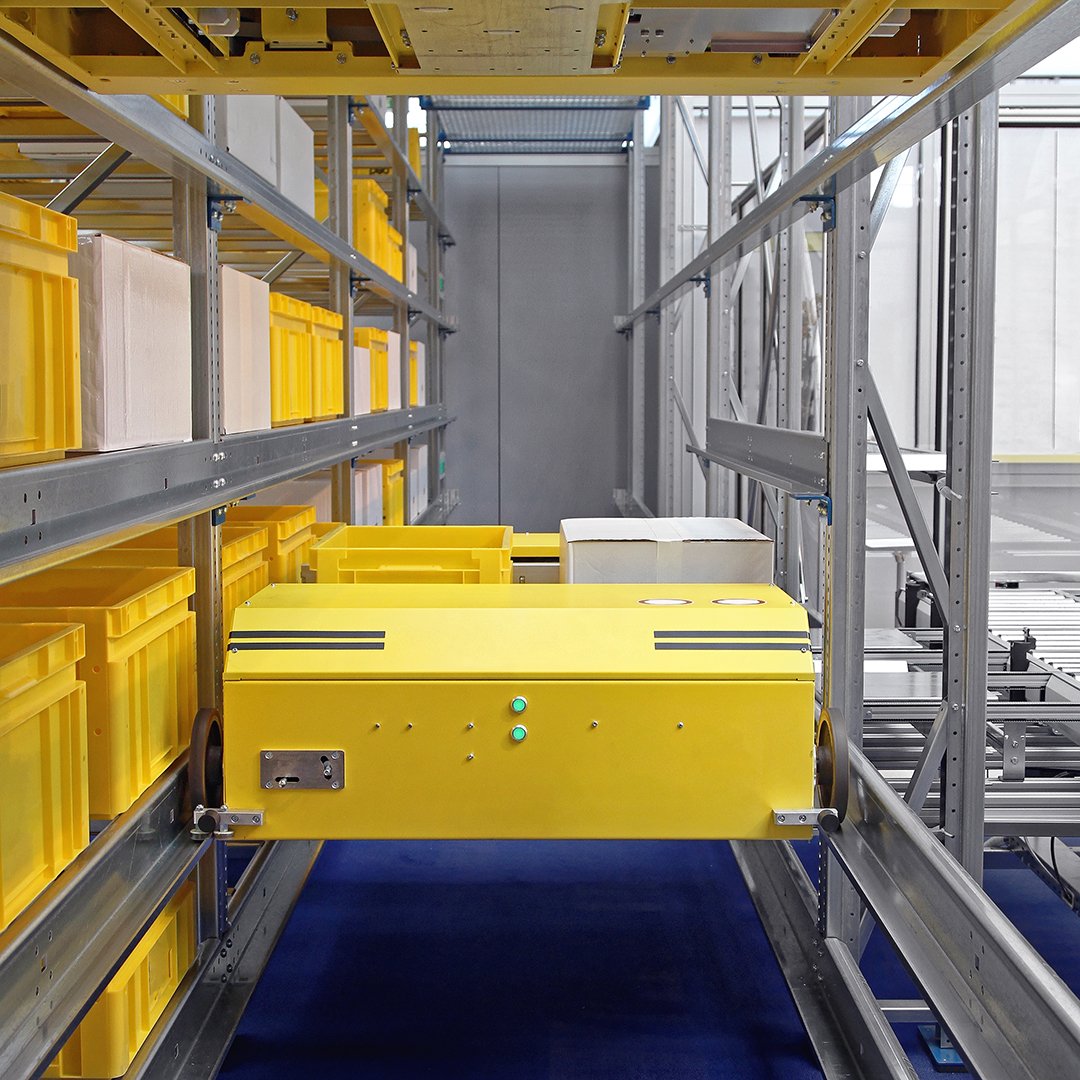

SHUTTLE SYSTEMS
Shuttle systems are made up of carts that operate on systems of racking with tracks. These shuttles move pallets between racks, and are capable of moving large loads very quickly. They can travel between levels of racks, allowing them to access a variety of products. However, shuttle systems are only able to retrieve entire pallets, and so they’re less efficient for warehouses that manage a variety of different inventory with a broad variety of throughput processing speeds.
Pros: Shuttle systems increase storage density and throughput, optimizing space in tight areas. They reduce human error by automating retrieval.
Cons: They can be expensive to install and are less efficient in environments with rapidly changing inventory or low system traffic.
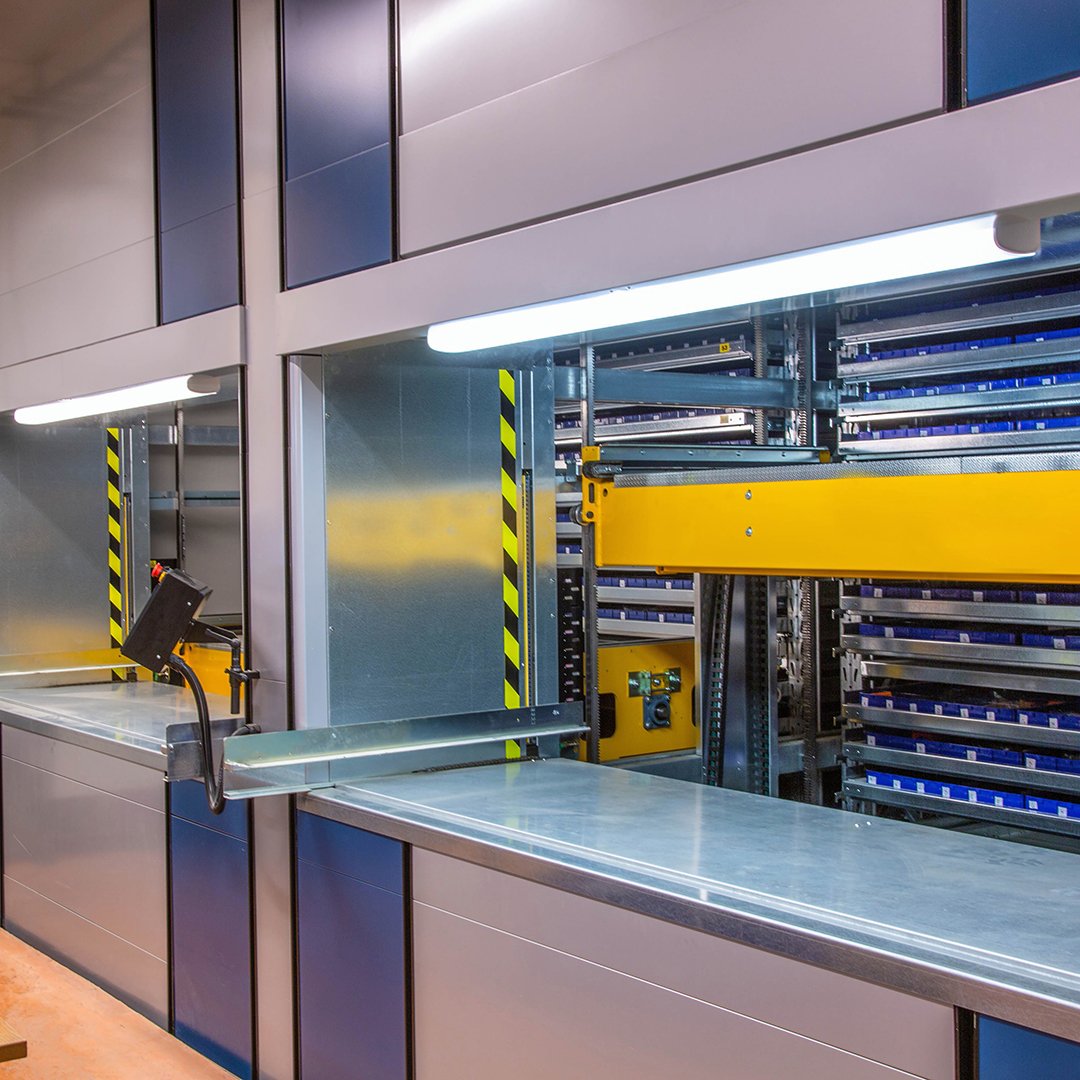

VERTICAL LIFT MODULES (VLM)
Vertical Lift Modules (VLM) are closed-storage systems that securely store trays on racks on either side of a retrieving mechanism. A VLM can be controlled by an operator or the warehouse management system (WMS). The selected tray is grabbed by the retriever and moved down the center to a picking window, where the operator is able to receive the tray without having to move to find and retrieve the items. The operator then selects the necessary items from the tray (often using a pick-to-light system or other automation to assist), before it is returned to storage.
Pros: VLMs make excellent use of vertical space and improve picking efficiency by delivering items directly to the operator. They are ideal for small or high-value inventory.
Cons: VLMs are not ideal for large or bulky items and may not perform well in high-volume environments due to their slower speed.
VERTICAL CAROUSELS
Vertical carousels are similar to VLM’s in that they are most frequently enclosed storage. However, instead of racks and a retriever like in VLMS, the trays of a vertical carousel are fixed to a rotating chain mechanism that rotates, bringing the attached trays to the picking window.
Pros: Vertical carousels save space and improve picking accuracy by bringing products to the operator. They are best for small items and high-mix environments.
Cons: They can be slower than other systems, and their fixed structure limits flexibility in rapidly changing operations.
HORIZONTAL CAROUSELS
Horizontal carousels contain shelves of products that rotate to face the operator. Pick-to-light systems are often utilized here as well to mark where the required product is located.
Pros: Horizontal carousels are flexible and efficient, providing good storage for a wide variety of products in a compact area.
Cons: They require more floor space than vertical carousels and may not be as fast in environments with high product turnover.

AUTONOMOUS MOBILE ROBOTS (AMR)
AMRs are a type of automated storage and retrieval system that are able to navigate without human guidance. They’re able to use sensors and cameras to make their way to products, select them, and transport them around an area. Depending on the size and capability of the AMR, they can transport boxes, trays, crates, totes, or pallets. They can be used in picking to bring items to operators, or can be used for security, maintenance, and inventorying purposes.
Pros: AMRs navigate autonomously, reducing the need for fixed infrastructure and improving flexibility. They integrate easily into existing warehouse operations.
Cons: They require additional infrastructure, such as charging stations and safety zones, and their performance can be affected by obstacles or layout changes.
For more information read about the Benefits of Warehouse Robotics.
OVERHEAD GANTRY SYSTEMS
Overhead gantry systems are infrastructures built into the ceiling of a warehouse. These systems select, manage, and transport stacked products like crates or pallets. They can be used for picking or for storage and organization.
Pros: Overhead gantry systems handle heavy or bulky items efficiently and improve safety by keeping products off the floor.
Cons: They require significant ceiling height and dedicated space, which may not be feasible in warehouses with low ceilings or limited space.
How are Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems Used?
Common Applications
GTP Picking: Most commonly automated storage and retrieval systems are used in goods-to-person environments to reduce the need for operators to manually find and retrieve product. GTP environments are designed so the operator remains at one workstation while the products are brought to them. AS/RS, controlled by the WMS or by the operator, are able to quickly find and retrieve products for operators, even from complex storage facilities.
Buffer Storage: AS/RS are used as buffer storage, meaning they’re used to store individual products, partially packed shipping orders, completed orders, or parts until they’re ready to be shipped or to move to the next part of the process. This allows for continuous order fulfillment, even when operators aren’t able to ship products or complete assembly from start to finish.
Secure/Controlled Storage Environment: AS/RS are often used for sensitive material that needs to be stored securely, or needs to be stored under specific circumstances. Because they utilize vertical space, AS/RS are able to store inventory securely and out of reach with safeguards on the WMS. The environments inside closed storage units like VLMs or vertical carousels are also able to be closely controlled and monitored for factors like humidity or temperature, making them ideal for a variety of uses, like the pharmaceutical industry.
Common Industries
Some form of automated storage and retrieval systems are used in most industries. Some of the most common industries where AS/RS is used are:
- Automotive
- Chemical
- eCommerce and Retail
- Manufacturing
- Mechanics & Parts
- Pharmaceutical
- Third-Party Logistics
- Warehouse and Distribution
What are the Benefits of Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems?
AS/RS can be very expensive. They take extensive infrastructure to implement and effort to maintain. AS/RS must be integrated with existing warehouse technology (WMS). Operators will need initial training, as well as continual updates and assessments to make sure they are using the systems correctly. However, the return is worth the investment for most facilities.
Some benefits of AS/RS include:
- Reduced Floor Space: AS/RS optimizes vertical space, allowing more storage in less floor area and reducing the need for additional real estate.
- Increased Efficiency: Automated picking reduces manual labor, speeds up retrieval times, and decreases human error, leading to higher throughput and lower labor costs.
- Improved Accuracy: Automation ensures precise picking, reducing mistakes and returns, which improves customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
- Higher Throughput: With faster, automated systems, AS/RS can handle high volumes of products quickly, increasing capacity and meeting growing demand.
- Customizable Design: AS/RS systems are flexible and can be tailored to fit various warehouse layouts, making them suitable for different industries and operational needs.
- Safety: By reducing manual handling, AS/RS systems minimize the risk of workplace injuries, creating a safer work environment.
- Scalability: AS/RS systems are easily adaptable and can grow with your business, accommodating changes in product types, inventory volume, or warehouse layout.
Is an Automated Storage & Retrieval System right for you?
If your facility is running into any of these problems, you should consider implementing an AS/RS.
- Running out of floor space?
- Struggling with order accuracy?
- Need to reduce labor costs?
- Unable to keep up with throughput and volume?
- Labor shortages?
MAVENEER IS READY TO HELP YOU
SELECT, MANAGE, DESIGN, AND IMPLEMENT AS/RS IN YOUR WAREHOUSE
©2026 Maveneer, LLC All Rights Reserved. Sitemap.